Science and Coding concepts
Biology Concepts
Urban Ecology
Urban ecology is the study of how living organisms interact with each other and with the natural and built environment in urban areas, as well as where and how organisms are distributed in urban areas.
Taxonomy
Wikipedia description of taxonomy
In biology, taxonomy (from Ancient Greek τάξις (taxis) ‘arrangement’ and -νομία (-nomia) ‘method’) is the scientific study of naming, defining (circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (division is sometimes used in botany in place of phylum), class, order, family, genus, and species.
The current system of taxonomy uses Latin names for the scientific name. Each scientific name can have multiple common names in multiple languages.
Here’s iNaturalist taxonomy for Western Fence Lizard, the most common species in Los Angeles City Nature Challenge.
Rank: Latin scientific name (English common name)
Kingdom: Animalia (Animals)
Phylum: Chordata (Chordates)
Class: Reptilia (Reptiles)
Order: Squamata (Snakes and Lizards)
Family: Phrynosomatidae (Phrynosomatid Lizards)
Genus: Sceloporus (Spiny Lizards)
Species: Sceloporus occidentalis (Western Fence Lizard)
In theory, every iNaturalist observation represents a species. In practice, an iNaturalist observation will be assigned to a particular taxa name and taxon rank based on the quality of the recorded data, the expertise of the observer, the suggestion algorithms of iNaturalist, and the expertise of people who help identify observations.
Coding Concepts
Programming is writing instructions for a computer to follow. We write these instructions in the form of code. There are hundreds of programming languages, each with its own vocabulary and syntax.
Geospatial concepts
Geospatial data is data that has a particular location. There are different software tools that can be used to display and analyze geospatial data.
Coordinate Reference Systems
Earth is a 3D sphere. Maps are 2D representation of a 3D sphere. Map projections are ways to flatten a spherical Earth to a flat surface.
The image belows shows maps of the United States in different projections. The differences in shape are a direct result of the calculations used to flatten the data onto a 2-dimensional map.
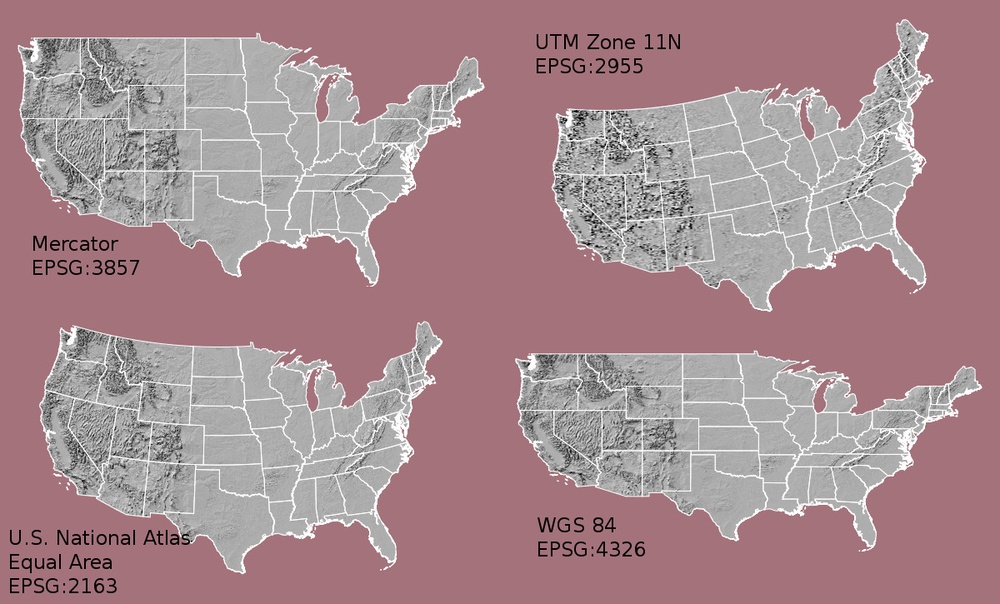
In order for software to correctly display and manipulate geospatial data, the data must include coordinate reference system (CRS) information. The CRS tells the mapping software which map projection to use and where the data is located. To make sure things line up when working with multiple geospatial data sets, it’s important to use the same CRS during data processing and analysis.